Thesis
-
Xie, D. (2022).
Bio-morphodynamics of coastal wetlands with mangrove vegetation.
(Doctoral dissertation, Utrecht University).
https://doi.org/10.33540/927

Journal Papers
-
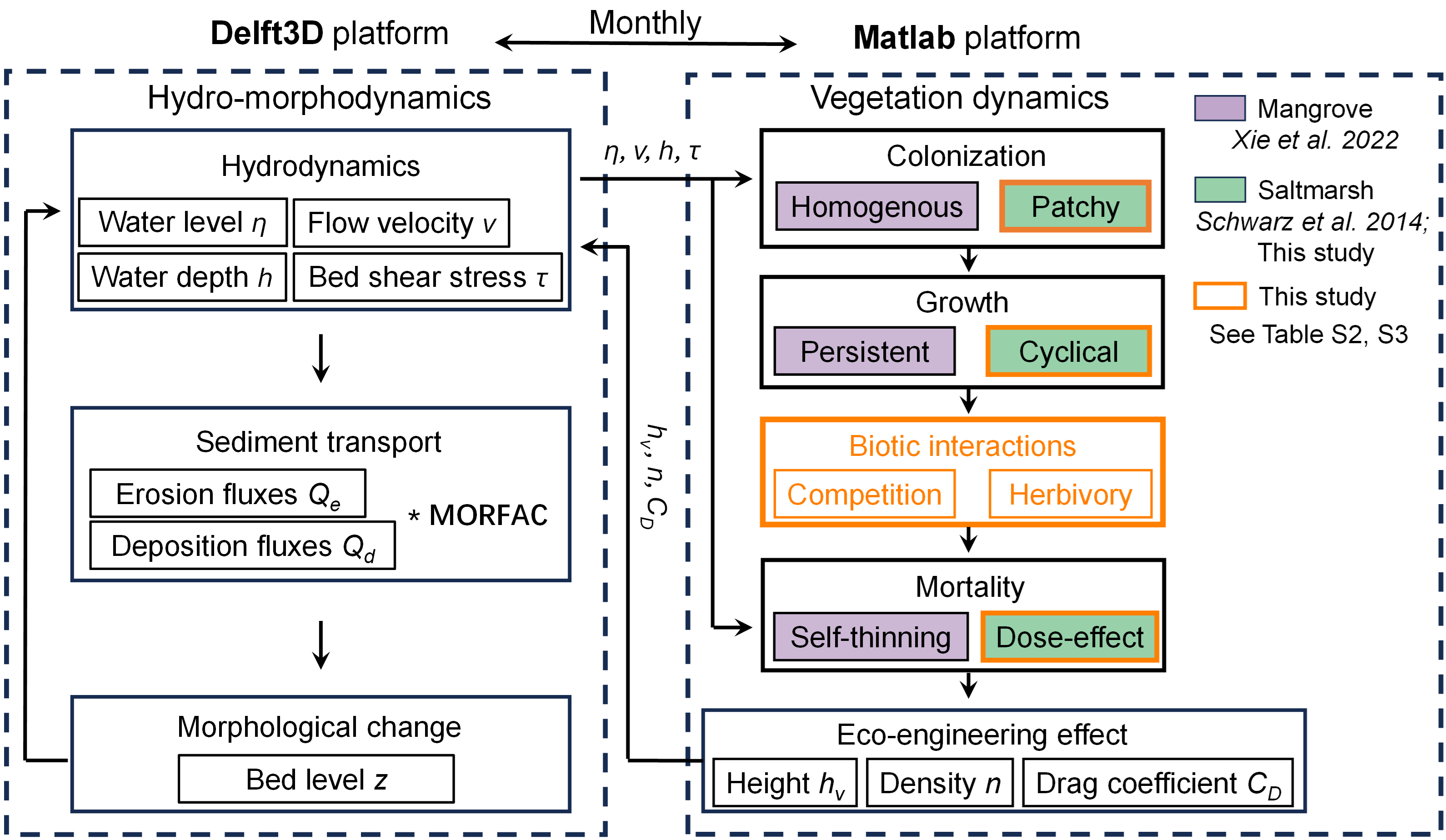
Wei, Y., van Maanen, B., Xie, D., Jiang, Q., Zhou, Z., and Schwarz, C. (2024).
Mangrove-saltmarsh ecotones: Are species shifts determining eco-morphodynamic landform configurations?
Earth's Future, 12(10), e2024EF004990.
https://doi.org/10.1029/2024EF004990
-
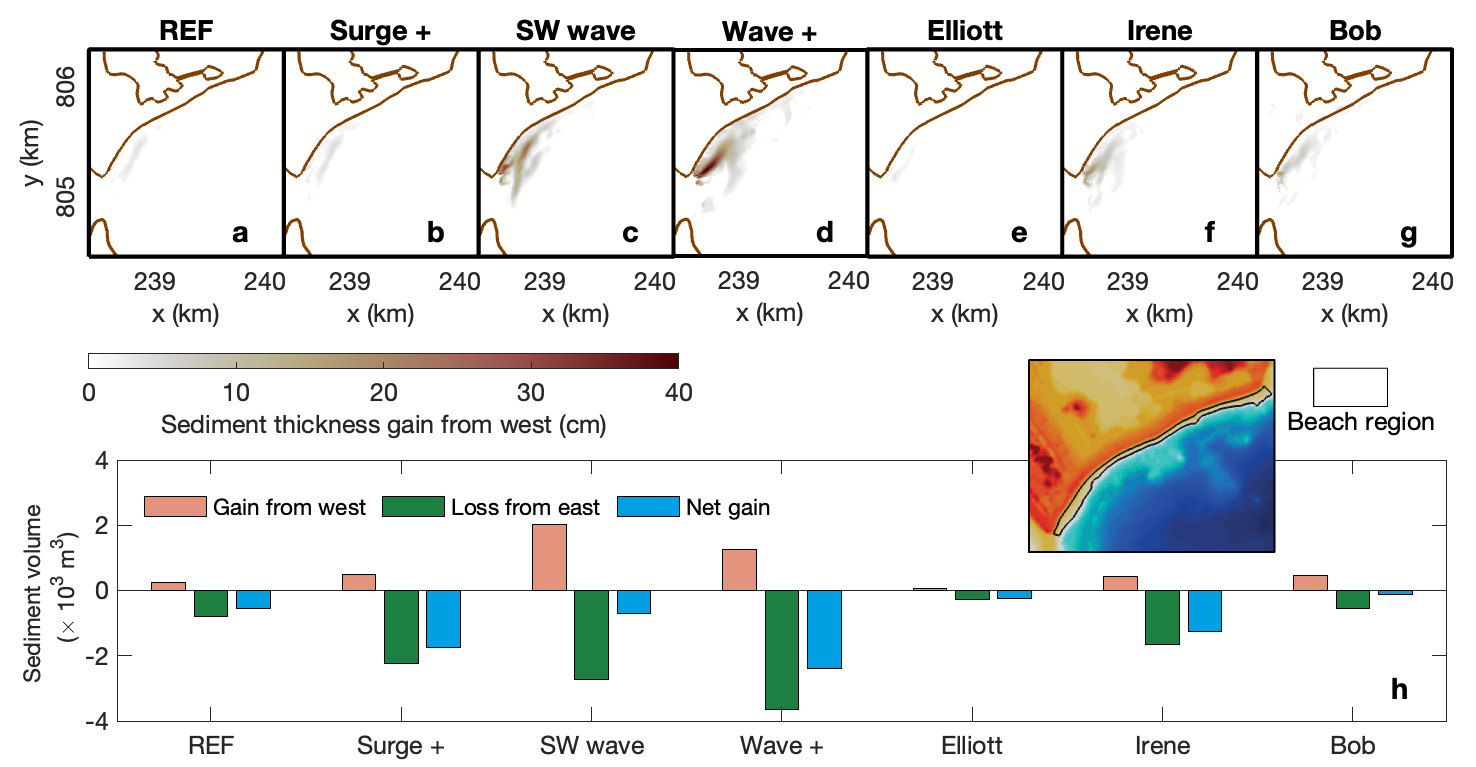
Xie, D., Hughes, Z., FitzGerald, D., Tas, S., Asik, T. Z., and Fagherazzi, S. (2024).
Longshore sediment transport across a tombolo determined by two adjacent circulation cells.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 129(10), e2024JF007709.
https://doi.org/10.1029/2024JF007709
-
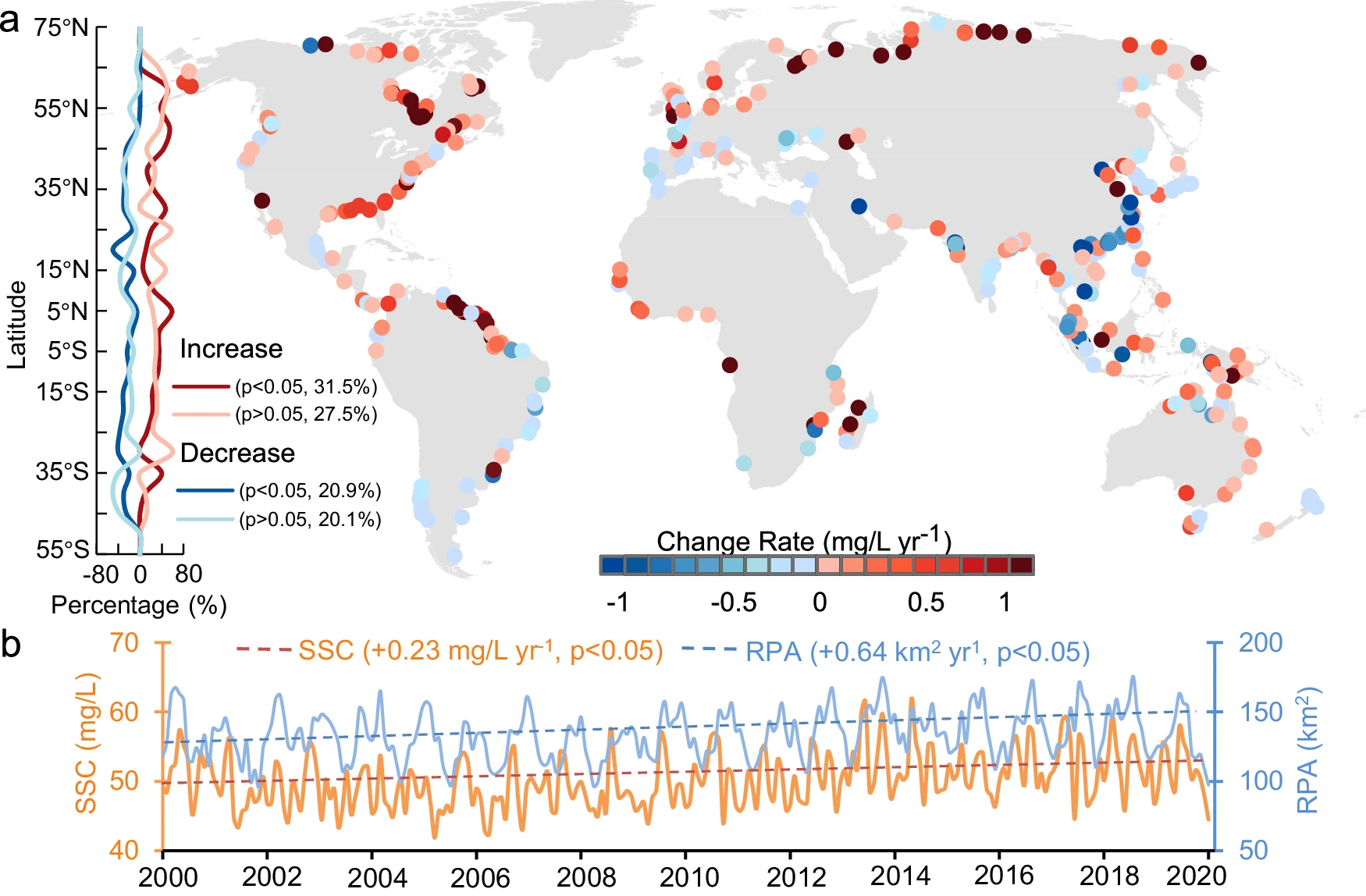
Hou, X., Xie, D., Feng, L., Shen F., and Nienhuis, J. (2024).
Sustained increase in suspended sediments near global river deltas over the past two decades.
Nature Communications, 15(1), 3319.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-024-47598-6
-
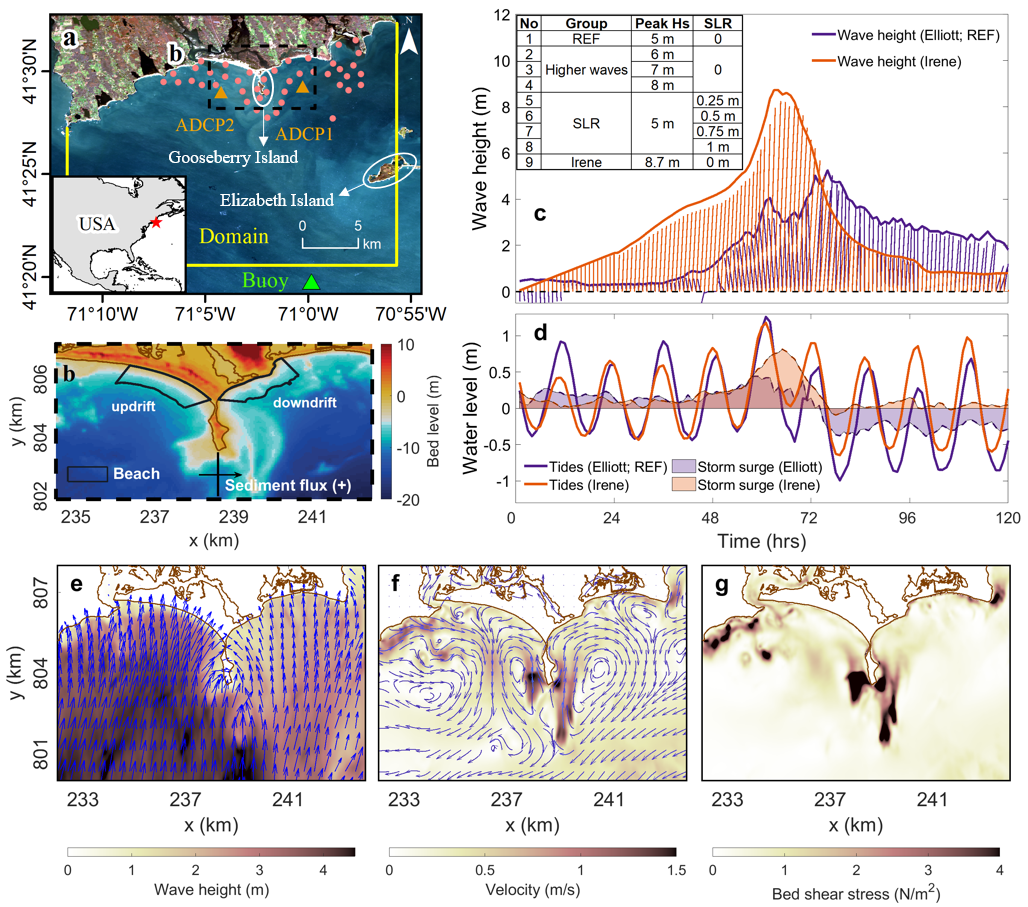
Xie, D., Hughes, Z., FitzGerald, D., Tas, S., Asik, T. Z., and Fagherazzi, S. (2024).
Impacts of climate change on coastal hydrodynamics around a headland and potential headland sediment bypassing.
Geophysical Research Letters, 51(4), e2023GL105323.
https://doi.org/10.1029/2023GL105323
-
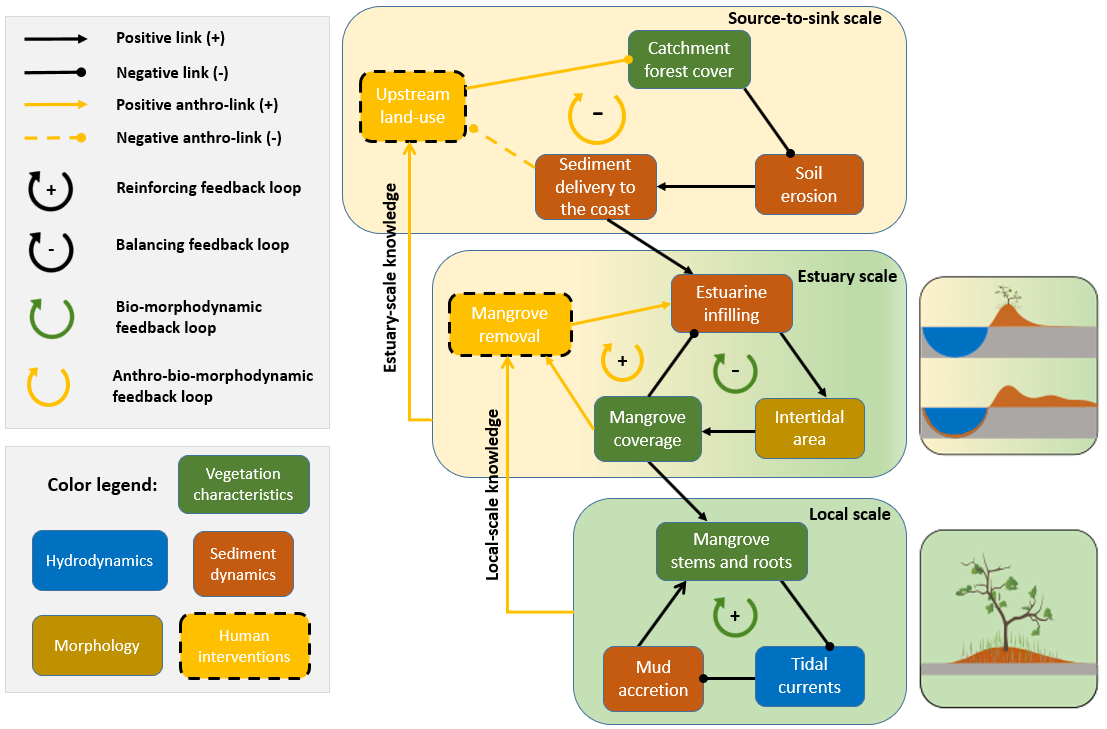
Xie, D., Schwarz, C., Kleinhans, M. G., Bryan, R. K., Coco, G., Hunt, S., and van Maanen, B. (2023).
Mangrove removal exacerbates estuarine infilling through landscape-scale bio-morphodynamic feedbacks.
Nature Communications, 14(1), 7310.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-42733-1
-
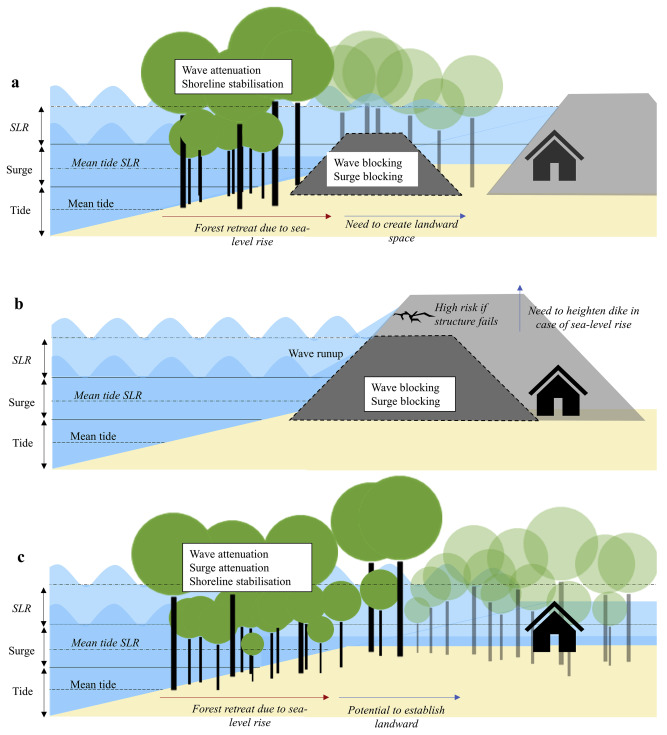
van Hespen, R., Hu, Z., Borsje, B., De Dominicis, M., Friess, D. A., Jevrejeva, S., ..., Xie, D. and Bouma, T. J. (2023).
Mangrove forests as a nature-based solution for coastal flood protection: Biophysical and ecological considerations.
Water Science and Engineering, 16(1), 1-13.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wse.2022.10.004
-
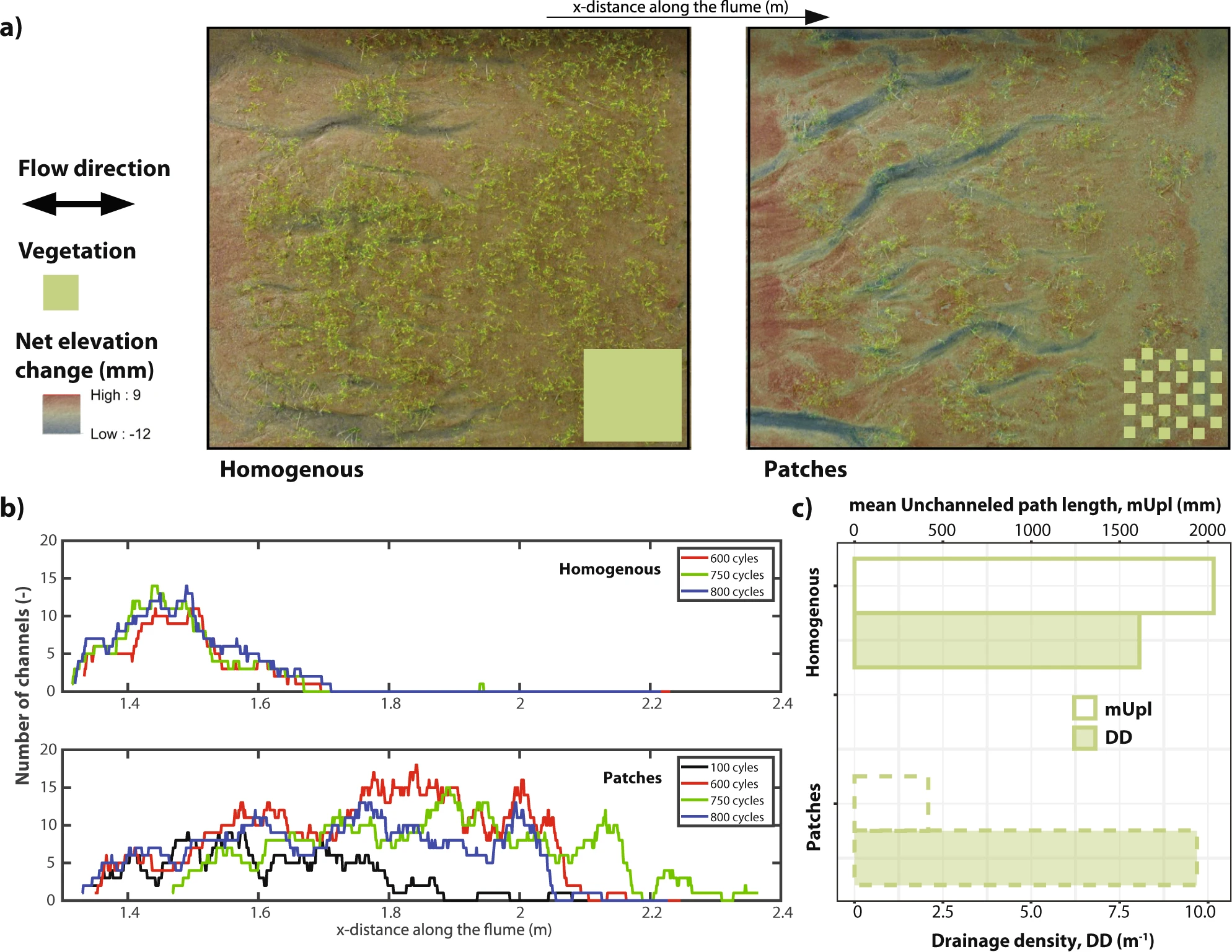
Schwarz, C., van Rees, F., Xie, D., Kleinhans, M. G., and van Maanen, B. (2022).
Salt marshes create more extensive channel networks than mangroves.
Nature Communications, 13(1), 2017.
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-29654-1
-
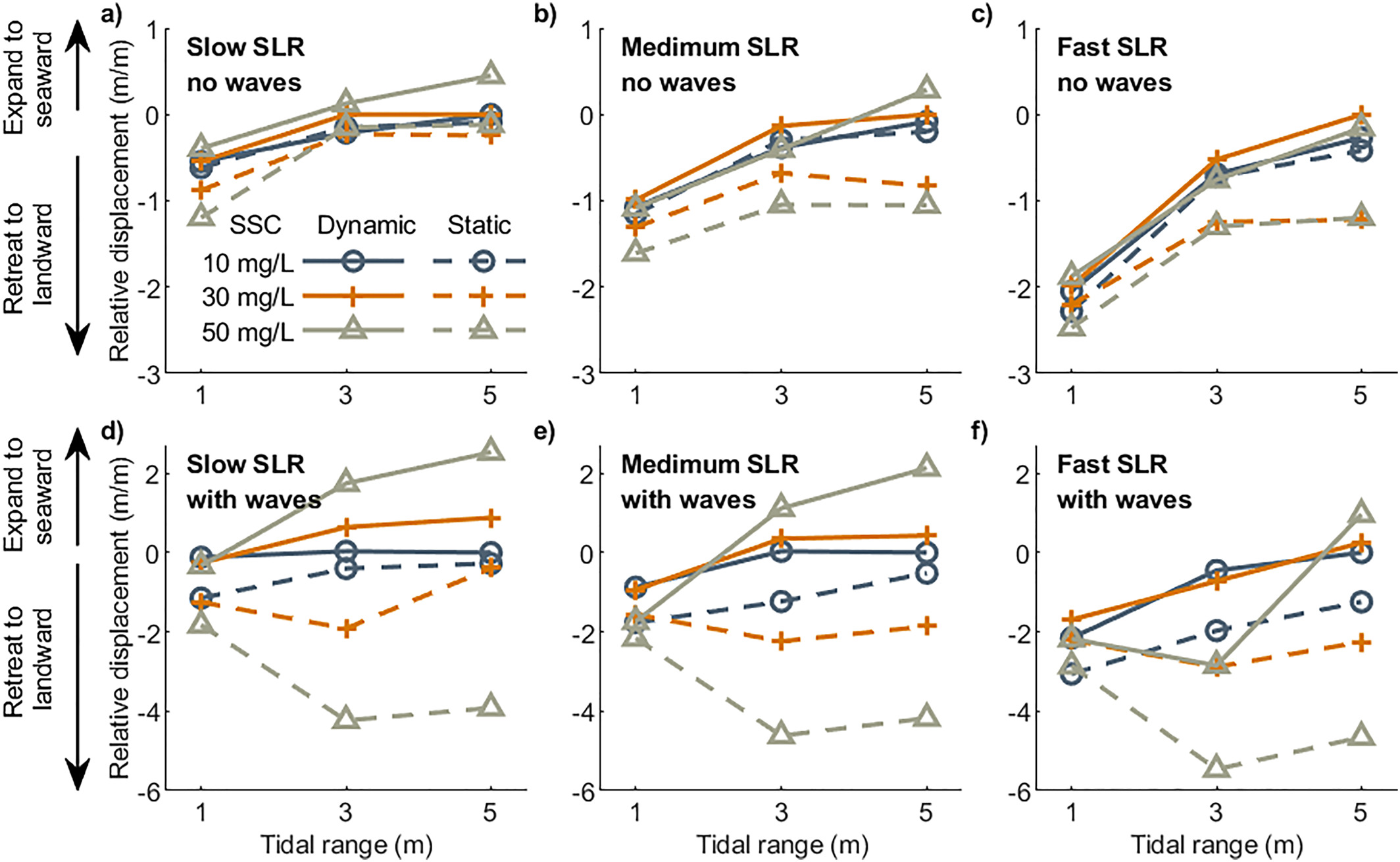
Xie, D., Schwarz, C., Kleinhans, M. G., Zhou, Z., and van Maanen, B. (2022).
Implications of coastal conditions and sea-level rise on mangrove vulnerability: A bio-morphodynamic modeling study.
Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 127, e2021JF006301.
https://doi.org/10.1029/2021JF006301
-
Xie, D., Schwarz, C., Brückner, M. Z. M., Kleinhans, M. G., Urrego, D. H., Zhou, Z., and van Maanen, B. (2020).
Mangrove diversity loss under sea-level rise triggered by bio-morphodynamic feedbacks and anthropogenic pressures.
Environmental Research Letters, 15(11), 114033.
https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/abc122
.jpg)
-
Xie, D., Tan, Y., Chu, A., Zhou, T., and van Maanen, B. (2020).
Distribution characteristics of the extreme storm tides in the radial sand ridges area of the South Yellow Sea in China.
Journal of Coastal Research, 85(sp1), 856-860.
https://doi.org/10.2112/SI85-172.1
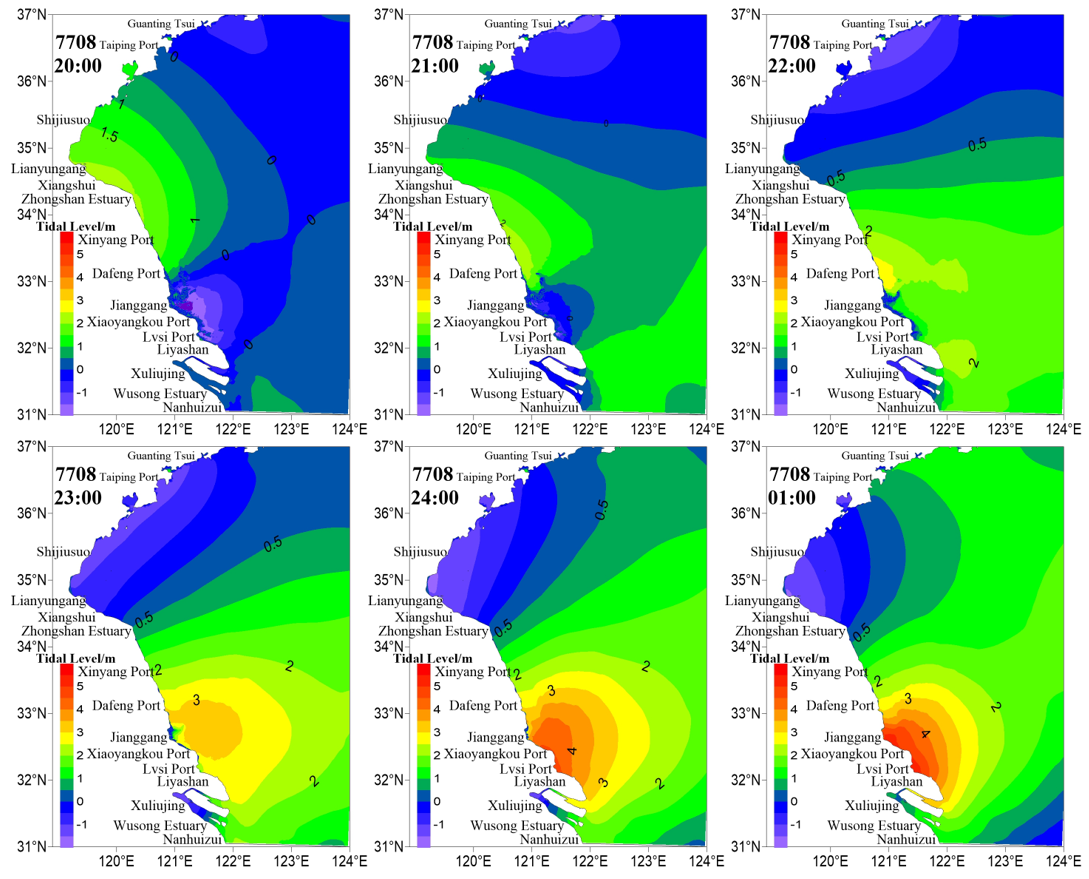
- Zhou, T., Tan, Y., and Xie, D.. (2018). Study on sea-level distribution of storm surges caused by cold wave in coastal areas of Jiangsu. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 30(4), 99-103. https://www.cabdirect.org/cabdirect/abstract/20193169601
- Tan, Y., Yang, F., and Xie, D.. (2016). The change of tidal characteristics under the influence of human activities in the Yangtze River Estuary. Journal of Coastal Research, 75(SI), 163-167. https://doi.org/10.2112/SI75-033.1
Conference Papers
- Xie, D., Tan Y., Chu A., and Zhang C. (2016). Analysis on the cause of the specific high tides in the South Yellow Sea. Proceedings of the Twenty-sixth International Ocean and Polar Engineering Conference, Rhodes, Greece, June 26-July 1, 1294-1299.
- Xie, D., Lin, j., Kuai, Y., Lu, T., and Zhou, Z. (2013). Summary on relationship between montmorillonite flocculation and seawater salinity. China Water Transport, 13(9), 120-122.
- Lu, T., Xie, D., Lin, J., and Kuai, Y. (2013). Effect of salinity on the hydrodynamic flocculation of montmorillonite. Logistics Engineering and Management, 35(8), 132-134.
- Lin, J., Xie, D., Lu, T., Kuai, Y., and Zhou, J. (2013). Effect of salinity on the flocculation of montmorillonite mineral. China Water Transport, 13(10), 121-124.